(Also known as CABG, pronounced “cabbage,” Coronary Artery Bypass Graft done via Open-Heart Surgery)
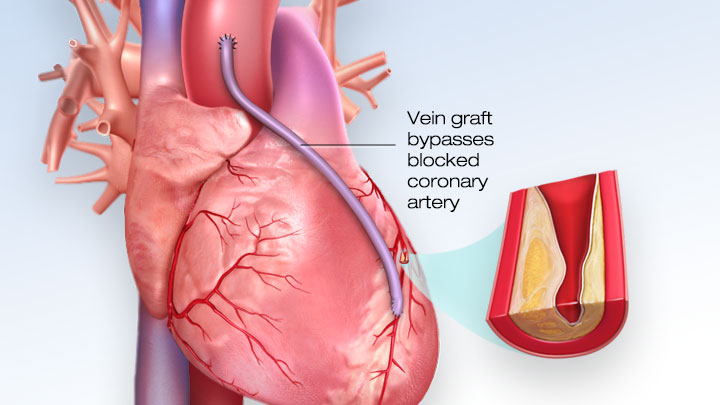
What the Procedure Does
Treats blocked heart arteries by taking arteries or veins from other parts of your body — called grafts — and using them to reroute the blood around the clogged artery to supply blood flow to your heart muscle.
A patient may undergo one, two, three or more bypass grafts, depending on how many coronary arteries are narrowed.
Requires several days in the hospital.
Reason for the Procedure
- One of the most common and effective procedures to manage blockage of blood to the heart muscle.
- Improves the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart.
- Relieves chest pain (angina).
- Reduces risk of heart attack.
- Improves ability for physical activity that has been limited by angina or ischemia.
Medications That Your Doctor May Prescribe Post-Procedure
Learn more about cardiac medications, including dual antiplatelet therapy, that you may need to take after your procedure to prevent complications and to put you on the path for the best recovery.
“https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-attack/treatment-of-a-heart-attack/cardiac-procedures-and-surgeries#”
